Вентилите се неопходни компоненти на јадрото во системите за контрола на течности, and correctly understanding and selecting the right Valve Pressure rating is fundamental to ensuring the safety and stability of the entire system. Incorrect selection can lead to valve leaks, damage, or even severe safety incidents. This guide will serve as an authoritative resource to systematically answer all key questions about valve pressure.
Содржина
ВклучиWhat is Valve Pressure?
Valve pressure refers to the maximum allowable pressure a valve can withstand at a specific temperature. This concept is typically understood on two levels:
- Номинален притисок (ПН): This is a reference value used for design, manufacturing, and application, representing the overall pressure-bearing capability of the valve. It is usually identified by “ПН” and is a standardized series. It does not mean the same working pressure can be maintained at all temperatures.
- Working Pressure: This is the actual fluid pressure the valve is subjected to in a real-world application at a specific operating temperature. The working pressure must always be less than or equal to the valve’s maximum allowable pressure at that temperature.

What are Valve Pressure Ratings?
А Valve Pressure Rating is a standardized classification system that categorizes a valve’s pressure-handling capability according to specific standards (like ASME, Во, API).
Concepts and Terminology of Different Valve Pressure Ratings
- Номинален притисок (ПН): The European standard system (Во 1092-1), based in Bars, is a series of reference numbers related to the valve’s mechanical strength.
- Class Rating (ЛБ): The American standard system (ASME B16.34, B16.5) is a series of classes based on the pressure can withstand at various temperatures. This is key to understanding the valve pressure rating meaning, as it is intrinsically linked to temperature. All types, from a gate valve pressure rating to a ball valve pressure rating, follow this system.
- API Pressure Ratings: The American Petroleum Institute (API) establishes pressure ratings for the oil and gas industry, како што е 2000, 3000, 5000, 10000 PSI in API 6A, which are defined working pressure ratings.

What are the Units of Valve Pressure?
- Bar: A common international unit of valve pressure. 1 Bar ≈ 1 atmosphere.
- MPa (Megapascal): The primary pressure unit in the International Valve System of Units (SI). 1 MPa = 1,000,000 Pa.
- Пси (Pounds per Square Inch): An imperial valve unit, very common in North America.
- kgf/cm² (Kilogram-force per square centimeter): A technical atmosphere unit.
How to Identify Pressure Markings on a Valve Body?
The markings cast or stamped on the valve body are the most direct way to identify its pressure capability. Common markings include:
- PN Rating: На пр., PN16, PN25, PN40. This indicates the nominal pressure rating of the valve in Bars and is a core identifier in the European (Во) standard system.
- Класа (or Pound Rating): На пр., 150ЛБ, CLASS 150, 300ЛБ. This is the pressure rating identifier for the American (Асме) standard system. The number does not directly correspond to PSI. A Class 150 valve does not mean it can only handle 150 Пси; its specific capability must be determined from the corresponding pressure-temperature rating chart.
- Тежина / CWP: На пр., 600 Тежина или 1000 CWP.
- Тежина stands for Water, Масло, Гас.
- CWP stands for Cold Working Pressure.
- Тежина / CWP are largely interchangeable and indicate the maximum pressure the valve can handle at ambient temperatures (typically -20°F to 100°F or -29°C to 38°C) for water, масло, and gas media. На пример, а brass ball valve pressure rating на “800 Тежина” means it can safely handle 800 PSI under cold, non-shock conditions.
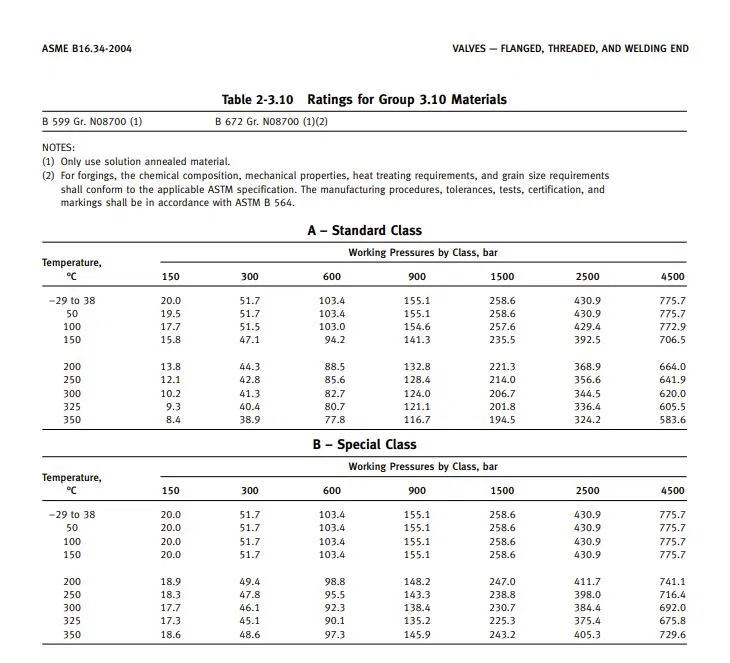
Working Pressures by Class– ASME B16.34-2004
How to Calculate Between Different Pressure Units?
Mastering unit conversion is essential for accurate calculations. Here are common valve pressure conversions:
- 1 MPa ≈ 145 Пси
- 1 Bar ≈ 14.5 Пси
- 1 Bar = 0.1 MPa
- 1 kgf/cm² ≈ 0.98 Bar ≈ 14.2 Пси
How to Convert Between Different Valve Pressure Ratings?
This is a critical and often misunderstood concept: There is no direct mathematical formula to convert between PN ratings and Class ratings!
This is because they are based on different standard systems, reference temperatures, and material groups. Сепак, for convenience in engineering applications, the following approximate correspondence chart can be referenced. This chart is for reference only; precise selection must be based on the specific standard.
Table 1: Valve Pressure Class vs. PN Rating Conversion Reference
| Class Rating | ПН (Номинален притисок) |
|---|---|
| Класа 150 | ПН 20 |
| Класа 300 | ПН 50 |
| Класа 400 | ПН 68 |
| Класа 600 | ПН 110 |
| Класа 900 | ПН 150 |
| Класа 1500 | ПН 260 |
| Класа 2500 | ПН 420 |
The Relationship of Valve Pressure-Temperature (P-T) Ratings
На Valve Pressure-Temperature Rating is the most important concept in valve selection. It dictates that the maximum allowable working pressure of a valve decreases as the operating temperature increases.
For all valves following ASME standards, the pressure rating is defined by a valve pressure temperature rating chart. This chart, based on the valve’s material (На пр., carbon steel A216 WCB, stainless steel A351 CF8M) и Class rating, details the maximum allowable working pressure at various temperatures.
For instance, a Class 150 carbon steel valve might handle close to 285 PSI at ambient temperature, but as the temperature rises to 300°C (572°F), its maximum allowable pressure could drop below 100 Пси.
What are the Key Factors Affecting Valve Pressure Ratings?
- Valve Body Material: This is the decisive factor. Different materials (Јаглероден челик, не'рѓосувачки челик, alloy steel, месинг) have vastly different mechanical strengths and creep resistance at various temperatures.
- Operating Temperature: As mentioned, temperature directly impacts material strength and thus dictates the valve’s pressure-handling capability.
- Design Standard: Different valve pressure rating standard documents (На пр., Асме, API, DIN) have different requirements for design, материјали, and testing.
- Connection Type: The strength and sealing performance of different connection types like flanged, welded, or threaded ends affect the overall pressure rating of the valve.
- Valve Type: The internal design of different valves, such as a check valve pressure rating versus a gate valve, means their potential weak points for pressure and sealing can differ.
Valve material, operating temperature and pressure comparison table
| Valve Material | Pressure (ПН) | Temperature | Media |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gray Cast Iron | ≤ 1.0 MPa | -10°C to 200°C | Вода, steam, air, гас, and oil products. |
| Malleable Cast Iron | ≤ 2.5 MPa | -30°C to 300°C | Вода, steam, air, and oil products. |
| Ductile Iron | ≤ 4.0 MPa | -30°C to 350°C | Вода, steam, air, and oil products. |
| Acid-Resistant High-Silicon Ductile Iron | ≤ 0.25 MPa | < 120°C | Corrosive media. |
| Carbon Steel | ≤ 32.0 MPa | -30°C to 425°C | Вода, steam, air, hydrogen, ammonia, nitrogen, and petroleum products. |
| Copper Alloy | ≤ 2.5 MPa | -40°C to 250°C | Вода, seawater, oxygen, air, oil products, and steam. |
| High-Temperature Copper (Легура) | ≤ 17.0 MPa | ≤ 570°C | Steam and petroleum products. <br> Note: Selection must comply with valve pressure-temperature standards. |
| Cryogenic Steel (Low-Temperature Steel) | ≤ 6.4 MPa | ≥ -196°C | Ethylene, propylene, liquefied natural gas (LNG), liquid nitrogen, etc. |
| Stainless Steel (Acid-Resistant) | ≤ 6.4 MPa | ≤ 200°C | Nitric acid, acetic acid, etc. |
How to Select the Right Valve Pressure Rating
Follow these steps for a scientific and safe selection process:
- Determine Operating Conditions: Clearly define the system’s maximum working pressure and maximum operating temperature. This is the foundation for selection.
- Select Valve Material: Choose the appropriate body and trim materials based on the fluid’s corrosiveness, температура, and other factors.
- Consult the P-T Rating Chart: Find the valve pressure rating chart corresponding to your chosen material.
- Verify and Apply a Safety Margin: On the chart, locate your maximum operating temperature and find the corresponding maximum allowable pressure. Ensure this pressure value is greater than your system’s maximum working pressure, and include a safety margin (typically 10%-25% is recommended).
- Finalize the Rating: Select a Valve Pressure rating whose P-T curve completely covers your operating point.
Пример: A system has a maximum working pressure of 45 Bar (approx. 653 Пси) and a maximum temperature of 300°C (572°F). The medium is steam, and the material is ASTM A216 WCB carbon steel. By consulting the ASME B16.34 standard, you would find that a Class 300 valve is rated for approximately 50 Bar at that temperature, whereas a Class 150 valve’s rating is far lower. Therefore, you must select a Class 300 or higher pressure rating.
Find Your Ideal Valve Solution – Optimize with BMAG







