Talaan sa sulud
MagtagadAko. Pasiuna: Ang mga balbula nga wala'y hinungdan - ang dili malikayan nga uso alang sa kahimsog ug regulasyon
1. What is a Lead-Free Valve?
Arte lead-free valve refers to a valve where the fluid-contacting components (such as the body, ball, or stem) are made from copper alloys containing an extremely low lead (Pb) content—typically ≤0.25% in early times, but now is ≤0.1%.
The core function is to ensure that drinking water supplies are not contaminated by lead as they pass through the valve, and to reduce the lead content in water, safeguarding public health.

2. Why the Need for Lead-Free Valves?
- Health Imperative: Lead is a toxic heavy metal. Chronic ingestion can cause severe damage to the nervous system and internal organs, particularly in children.
- Regulatory Compliance: Major global markets have mandated strict standards for materials that come into contact with potable water.
3. Global Policies Driving Lead-Free Adoption
- The United States: The most significant regulation is the SDWA-1417 (Safe Drinking Water Act), which took effect in January 2014. This law mandates that the wetted surface of any device used for conveying or dispensing potable water must contain no more than 0.25% lead. Certification NSF / ANSI 372 is required.
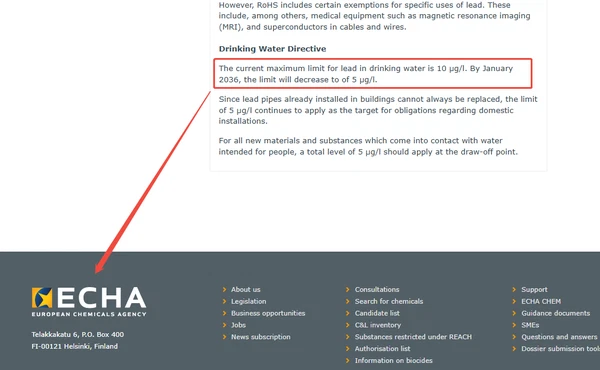
- Europe: The European Union’s revised DWD(Drinking Water Directive), implemented in Enero 2021, sets the maximum acceptable concentration for lead in drinking water: 10 µg/L. DWD sets a new limit of 5μg/L, which must be achieved by all EU member states by 2036. Member states enforce this through national certification schemes, often requiring materials to contain less than 0.1% lead.
II. Ang “Manguna” Mystery in Copper Alloys: Kalihokan, Hazard, and Substitution
1. The Role of Lead in Traditional Brass Alloys
In traditional brass alloys, lead exists as an insoluble phase at the grain boundaries. Its primary function is to enhance the machinability (making the alloy easier to turn, drill, and shape) while also increasing lubricity ug Pagsul-ob sa Pagsukol.

2. Can lead in copper alloys be substituted?
- The Challenge: When lead is removed, how can the alloy maintain sufficient machinability, mechanical strength, and corrosion resistance?
- Lead Substitution Elements: The main alternatives include:
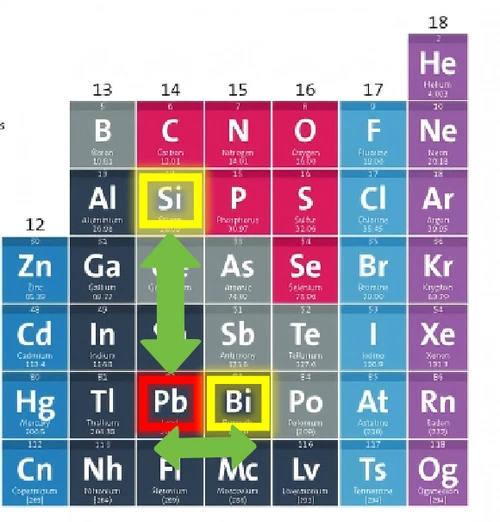
- Bismuth (Bi): Forms a low-melting-point phase that greatly improves chip breakability and is the most common substitute today.
- Silicon (Ug): Increases strength and corrosion resistance (especially dezincification resistance) and can also aid in machinability.
As illustrated in the diagram below, both silicon and bismuth are in proximity to lead on the periodic table and share analogous atomic structures, which results in similar material properties.
III. Which Lead-Free Copper is Best for Valves?
1. Key Performance Requirements for Lead-Free Valve Alloys
- Ultra-Low Lead: Must satisfy regulatory limits ≤0.1%.
- Corrosion Resistance: Crucial for longevity.
- Strength & Pressure Rating: To ensure long-term operation.
2. Recommended Lead-Free Grades and Comparison
Bmag highlights Bismuth Brass ug Silicon Brass as the leading choices for manufacturing high-performance, lead-free copper valves.
- C89833 (Bismuth Brass): Excellent castability, making it a premier choice for cast valve bodies.
- C87800 (Silicon Brass): Outstanding strength and exceptional resistance to dezincification corrosion.
- C69300 (Silicon Brass / EcoBrass): A high-strength, high-performance option favored for forged valve bodies and balls.
- CW511L (Low-Lead Brass / Low Lead-Free): Often used where lead restrictions are less strict, or for cost-sensitive applications.
| Listed Grade | Rehiyon | Primary Characteristics / Application |
|---|---|---|
| C89833 | ASTM | Cast Lead-Free Bismuth Brass, suitable for potable water |
| C87700 | ASTM | Cast Silicon Brass |
| C87800 | ASTM | Cast Silicon Brass |
| C69300 | ASTM | High-Performance Silicon Brass, Forging |
| C87850 | ASTM | Cast Bismuth-Silicon Brass |
| CW509L | EN | Low-Lead Wrought Brass |
| CW510L | EN | Low-Lead Machinable Brass |
| CW511L | EN | Low-Lead Machinable Brass |
2. US UNS and European EN Naming Rules
- US UNS (Unified Numbering System): Uses the format “C” + 5 digits. C8xxxx series denotes Cast copper alloys, while C1xxxx through C7xxxx denote Wrought (deformed/forged) copper alloys.
- European EN (Euro Norm): Uses the format “CW” + 3 digits + letter. “C” for Copper, “W” for Form (W-Wrought, B-Cast), and the suffix “L” (for Low Lead) often indicates compliance with modern standards.
V. How to Choose a High-Quality Lead-Free Valve Supplier
1. Ang “Golden Rules” for Supplier Selection
- Rule 1: Verify the Material Test Certificate (MTC): Demand a complete Mill Test Certificate or chemical composition report for the raw materials. Ensure the lead (Pb) content strictly adheres to the required market regulations.
- Rule 2: Check Third-Party Certifications: Confirm that the final valve product holds necessary potable water contact certifications (such as NSF/ANSI 372, UPC, ACS, or WRAS).
- Rule 3: Assess Manufacturing Process: Premium lead-free alloys require advanced casting and/or forging technologies. Choose a supplier with proven expertise in these specialized manufacturing techniques.
- Rule 4: Check Migration Testing: The valve product has passed the final compositional migration testing.
2. BMAG’s Quality Guarantee
Bmag is committed to using high-quality, certified lead-free copper grades. We provide all necessary raw material documentation and product certifications, giving you complete confidence in your supply chain.
VI. Take Action Now: Contact BMAG for Your Expert Lead-Free Valve Solution
Bmag delivers reliable, code-compliant lead-free copper valves that meet the highest global health standards. Whether you are navigating regulations in North America, Europe, or other demanding markets, Bmag offers the most reliable and cost-effective solutions.
Contact the BMAG expert team today for your project’s specialized material reports and lead-free valve solutions!
Related article: EU nag-inom sa direktiba sa tubig (DWD): Ang mga balbula nga balbula nga wala'y hinungdan






